Modern materials used in furniture production are very diverse and allow you to create furniture of the most varied quality and appearance. The most common materials today are laminated chipboard and MDF. Let’s figure out what their differences are and what is better for you when choosing furniture.
MDF (fine fraction) is a panel material made by dry pressing fine wood chips at high pressure and temperature.
This material arose due to the improvement of technologies in the manufacture of fiberboard. Additional synthetic binders are not used in MDF. The natural material lignin, which is part of the wood, acts as a binder. Therefore, MDF is an environmentally friendly material.
In the production process of MDF, special properties can be imparted: hardly combustible, biostability, water resistance. MDF is used to produce cabinets, kitchen, office furniture, non-standard furniture, trade equipment, and doors.
Also, MDF is a high-tech material. Its surface is easy to process, and MDF parts can be given the most varied and unusual shapes. MDF can be easily painted and laminated, laminated, molded, suitable for thin veneer veneering, imitation printing, varnishing, and enamel coating. And MDF with frequent milling grooves bends well. It also has a high level of noise absorption and sound insulation and excellent thermal insulation properties.
Chipboard is particleboard. Sheet material, for the production of which fine wood particles are mixed with a binder (resin) and hot pressed.
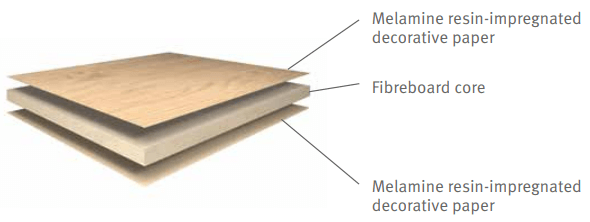
Chipboard – laminated chipboard, the surface of which is lined with a special film made of thermosetting polymers. At first, this film looks like ordinary paper, which is impregnated with melamine resin, then by pressing the film is “tightly” connected to the surface of the chipboard. Thanks to such cladding, the appearance of the chipboard is much improved, the reliability, wear resistance, resistance to chemical influences, moisture, low temperatures increase. Since the coating limits the evaporation of harmful vapors of substances contained in the chipboard, the chipboard with lamination is more environmentally friendly for others.
There are many variations of the slab coating structures. Chipboard can be smooth and embossed, that is, imitation of various materials’ structure on the slab’s surface: wood, shagreen, etc. Many color options are also possible: various types of wood, all kinds of background textures, metallic colors, and just different colors. Due to its simplicity in processing and a huge assortment, laminated chipboard has become almost the main material in furniture production.
How to distinguish MDF from chipboard?
First, let’s figure out how these names are deciphered. MDF – fine wood fraction, and chipboard – laminated chipboard. Both are made from wood waste, but the properties of these materials are different. Chipboard is made from larger chips. Therefore, distinguishing it from MDF is enough to look at the cut and pay attention to the structure. If you see sawdust there, you have a chipboard in front of you.
Chipboard production? How to define quality?
For chipboard production, sawdust and shavings are pressed and impregnated with formaldehyde resins for gluing, and the resulting board is usually laminated with melamine film. The letter “L” at the starting of the sentence abbreviation indicates that the chipboard is laminated. The film protects the board from moisture and other external influences and prevents the release of formaldehyde into the external environment.
There is a safety classification for laminated chipboard based on the concentration of formaldehyde:
- E1 – formaldehyde emission class, which is considered safe for the production of furniture (such a plate is made according to European standards;)
- Class E2 – strictly prohibited for use in the production of children’s furniture;
- Class E 0.5 – also complies with European quality standards. However, its use is not always necessary since the film prevents the evaporation of the harmful compound;
- E 3 – strictly prohibited for use in production.
When buying furniture, be sure to ask the seller for the safety class and ask for certificates.
How is MDF made? How to define quality?
For the production of MDF, wood is crushed, dried, and pressed. Lignite, a natural substance found in wood, binds wood particles together instead of resins. There is practically no formaldehyde in MDF, and in terms of chemical safety, the material is as close as possible to natural wood. For protection, a PVC film, veneer, or enamel is applied to it.
Which is more robust – MDF or chipboard?
MDF is denser, not only chipboard but also a solid array. High humidity isn’t a problem for this material. Therefore it is suitable for use in the bathroom or kitchen. MDF is a more flexible material. Consequently, furniture of complex streamlined shapes is made from it. It also produces deep mills and patterns well due to its fine structure and high density.
Chipboard is less durable than solid wood and MDF. It is not recommended to use it in bathrooms and the kitchen because moisture can seep inside through cuts and detachments on the film. This causes swelling, change in shape, and further reduces strength.
| MDF | Chipboard | |
| Surface: | Laminated | Many processing methods – painted, plastic or film-coated, laminated, etc. |
| Fine processing capability: | None (you cannot make deep milling, complex curly details) | Details from MDF can be given the most diverse and unusual shape. |
| Strength: | Resistance to a variety of mechanical damage | High material strength (superior to natural wood) |
| Environmental resistance: | High thermal shock resistance | High resistance to moisture, fungi, and microorganisms, high-temperature steam |
| Colors and textures: | A wide variety of colors and textures | A wide variety of colors and textures |
| Price: | Average | High |
| Environmental friendliness: | Average | Environmentally friendly material |
| Flaw: | Inability to make curved facades | The standard size of facades (expensive custom-made sizes) |
What is cheaper than MDF or chipboard, and why?
MDF costs one and a half to two times as much as plywood. More expensive than chipboard and is used for the premium and luxury segments. Economy segment products are always made from laminated chipboard. The finishing material can influence the final cost of a product. PVC film and sheet plastics are the most cost-effective. Enamel is a little more expensive than porcelain. The natural veneer is the most expensive finish.
Which material is suitable for which room?
The advantages of MDF are apparent, but it is an expensive material, so furniture is seldom made entirely of MDF. Manufacturers see no technological sense in spending this way. Often the body is made of laminated chipboard, and the facades are made of MDF.
This allows you to keep quality at a reasonable price. You do not overpay for expensive MDF where it is not needed.
So how do you choose the material for your furniture?
Here’s our memo in the form of simple theses:
- Chipboard is perfect for the living room and hallway. Just make sure that the stove is of high quality. Request a certificate confirming the class of the board.
- The combination of chipboard and MDF is suitable for children’s and bedrooms, but the rule is the same: the material must be of a high class, and the product must be well glued, including edges and joints.
- It is more correct for the kitchen and bathroom to choose MDF: It is most frequently exposed to temperature and humidity variations in these settings.
Which is better: MDF or chipboard?
When buying kitchen, office, or school furniture, dressers, and wardrobes, the question arises as to what is better than MDF or chipboard as a material for producing this furniture. It is simply unrealistic to choose, focusing only on appearance, since finished products from these materials practically do not differ from each other. Meanwhile, there are still differences between them.
Technological features of the production of MDF and chipboard
One of the main differences between these materials can be considered the raw material for their production. As you know, chipboard is made from small shavings and sawdust by mixing this mass with glue and pressing. In this case, the adhesive usually contains a certain amount of epoxy resin and formaldehyde, the evaporation of which can be harmful to human health.
In turn, MDF boards are made from fine wood chips, practically from wood flour. Much less adhesive is required for its gluing, on which the environmental friendliness and safety of MDF material ultimately depend. Also, a distinctive feature of MDF is its density, which almost matches the density of natural wood.
Performance characteristics of MDF and chipboard
The main advantage of chipboard boards is their endurance, the ability to withstand significant loads during operation. Also, the low cost made the production of chipboard furniture popular among most furniture makers. However, it is no secret that chipboard is afraid of water. High and constant humidity in the room where furniture made of this material is installed will inevitably lead to the chipboard crumbling. And the ingress of water directly under the decor layer (laminated film or veneer) will cause swelling and softening inside the board. All this will have a detrimental effect on the appearance of the furniture.
MDF also has several features. Furniture manufacturers have long appreciated its extraordinary versatility. MDF during processing can be given any shape. Despite the decent thickness of the slabs, they can be bent, patterns and designs can be applied. This material is not as sensitive to water and moisture as chipboard. In addition, the indisputable advantage of MDF is its hygiene and complete immunity to all kinds of fungi. But this material reacts very painfully to temperatures above 70 degrees Celsius. It swells, shrinks, loses its shape, and the decorative coating bubbles and peels off. That is why MDF furniture is recommended to be protected from heating and not placed near a working stove, oven, or other heating devices.
Thus, when deciding what is better than MDF or chipboard, it is necessary to consider their quality characteristics and the specific operating conditions.